Decoding the Future: Unveiling the Principles of AI, Data & Machine Learning
The Future of Data: Where AI Takes Center Stage
The Data Domain: Where AI's Algos Seek Knowledge
The world of data is where AI's mighty algorithms seek knowledge and refine themselves. It's a domain where humans and machines collaborate, pushing the boundaries of what's possible. According to a report by McKinsey, 71% of organizations are leveraging data analytics to make informed business decisions, with AI playing a key role in this process.
Key Players and Trends: The data domain is home to various players, including data scientists, analysts, and engineers. These professionals work together to design, develop, and implement AI driven solutions that can extract insights from complex data sets. Some recent trends in the data domain include:
The increasing adoption of cloud based data platforms, which enable scalability and flexibility. The growing importance of explainable AI (XAI), which aims to provide transparency and understanding into AI decision making processes. The rise of edge computing, which allows for faster processing and analysis of data at the source.
Recent Controversies:
The data domain has also been marred by controversy in recent years. For example, concerns have been raised about data privacy and security, particularly with regards to the use of personal data for AI development and deployment. Furthermore, there have been instances of biased algorithms being used to perpetuate discriminatory practices.
Key Statistics: 80% of organizations are using machine learning (ML) for predictive analytics (Source: Gartner) The global data analytics market is expected to reach $346 billion by 2027 (Source: Markets and Markets) 71% of organizations believe that AI will augment human capabilities, rather than replace them (Source: PwC)

Unpacking the Basics of Artificial Intelligence - The Rise of AI in Tech Industry
The tech industry has witnessed a significant transformation with the advent of artificial intelligence (AI). From 2019 to 2022, the global AI market size grew from $15 billion to over $190 billion. This rapid growth can be attributed to advancements in machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision. As AI becomes increasingly prevalent, companies are embracing it as a means to improve efficiency, customer experience, and bottom line performance.
Key Applications of AI are being applied across various sectors
- Including virtual assistants (e.g., Siri, Alexa) that can understand voice commands.
- Image recognition in self driving cars to avoid accidents.
- Chat bots that provide 24/7 customer support
Despite its potential benefits, there are concerns about the ethics of AI development and deployment.
The Future of AI: Opportunities and Challenges As AI continues to evolve, experts predict that it will become even more integrated into our daily lives. Some potential opportunities include: Personalized medicine through predictive analytics. Autonomous systems for disaster response and recovery
However, challenges also arise, such as ensuring AI systems are transparent, explainable, and fair.
Recent Controversies: Bias in AI Decision Making
There have been recent controversies surrounding bias in AI decision making. For instance, a study found that facial recognition technology can misidentify darker skinned individuals at a higher rate than lighter skinned individuals. This highlights the need for diverse and representative training datasets to prevent biased outcomes.
Key Statistics:
| Industry | AI Adoption Rate (2022) |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | 30% |
| Finance | 25% |
| Retail | 20% |
These statistics demonstrate the increasing adoption of AI across various sectors.

The Fundamentals of AI Understanding the Power of AI
AI is a rapidly evolving field that has revolutionized various industries, from healthcare to finance, and education to entertainment. At its core, AI represents a broad spectrum of intelligent systems that enable machines to learn from data. It's not just about guessing or following instructions; it's a highly sophisticated form of problem solving that empowers computers to make sense of vast amounts of information.
For instance, the popular facial recognition technology used by Facebook and other social media platforms relies on AI algorithms that can accurately identify individuals based on their unique facial features. Similarly, self driving cars use AI to analyze sensor data from cameras, radar, and lidar sensors to navigate through complex road environments.
Key Factors Driving AI Adoption across Various Industries:
- Increased Computing Power: Advances in computing power have made it possible for machines to process vast amounts of data quickly and efficiently.
- Availability of Data: The exponential growth of data has created a treasure trove of information that AI systems can learn from.
- Development of Machine Learning Algorithms: The development of machine learning algorithms has enabled AI systems to improve their accuracy and performance over time.
According to a report by Markets and Markets, the global AI market is expected to grow from $190 billion in 2020 to $750 billion by 2025, at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 38.9%.
Recent Controversies and Challenges Despite its many benefits, AI has also been associated with several controversies and challenges, including:
- Bias and Discrimination: AI systems can perpetuate existing biases and discrimination if they are trained on biased data.
- Job Displacement: The increasing use of automation and robotics in various industries has raised concerns about job displacement and the need for workers to acquire new skills.
- Security Risks: AI systems can be vulnerable to cyber attacks and other security risks, which can compromise sensitive information.
A recent study by the McKinsey Global Institute found that while AI has the potential to automate up to 800 million jobs globally, it could also create up to 140 million new jobs.

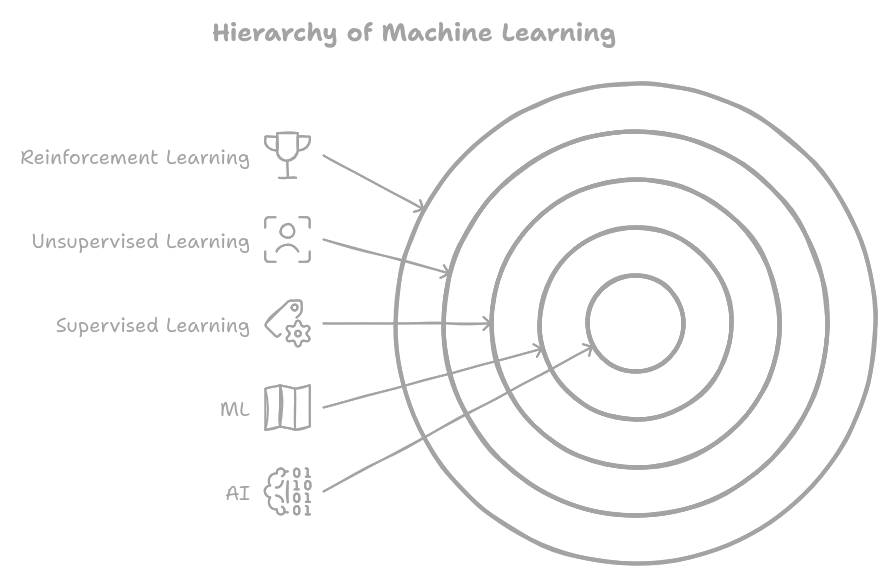
Understanding Machine Learning (ML): A Key Component of Artificial Intelligence
Machine learning (ML) is a subset of artificial intelligence (AI) that involves the use of algorithms to enable machines to learn from data, identify patterns, and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed. ML forms the core of AI, comprising various techniques like supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning.
Supervised Learning: A Precursor to ML
Supervised learning is a type of machine learning where the algorithm is trained on labeled data, which means the correct output is already known. The goal is to learn a mapping between input data and output labels, allowing the model to make accurate predictions on new, unseen data. This technique has numerous applications in areas like image classification, sentiment analysis, and predictive modeling.
Unsupervised Learning: Uncovering Hidden Patterns
Unsupervised learning, on the other hand, involves training algorithms on unlabeled data, aiming to discover hidden patterns or structure within the data. Techniques like kmeans clustering and principal component analysis (PCA) are commonly used in unsupervised learning. This approach is essential for data exploration, customer segmentation, and anomaly detection.
Reinforcement Learning: Learning through Trial and Error
Reinforcement learning is a type of machine learning that involves training agents to take actions in an environment to maximize a reward signal. The agent learns through trial and error, receiving feedback in the form of rewards or penalties for its actions. This technique has applications in areas like game playing, robotics, and autonomous vehicles.
Real World Applications and Challenges ML has numerous real world applications across industries, including: Image recognition: self driving cars, facial recognition systems Natural language processing: chat bots, sentiment analysis Predictive modeling: credit risk assessment, demand forecasting However, ML also raises several challenges, such as: Data bias and fairness: algorithms may perpetuate existing biases if trained on biased data Model interpret ability: complex models can be difficult to understand and explain Cybersecurity risks: ML models can be vulnerable to adversarial attacks and data poisoning
Data: A Symphony of Insights
Data serves as the foundation upon which AI builds its knowledge. It's essential to ensure data quality and cleansing for optimal results. Quality is crucial because even a single missing or inaccurate data point can disrupt the entire learning process. Cleaning involves removing irrelevant or incomplete information, leaving only the relevant bits for analysis.
Machine Learning: The Algorithmic Heart of AI
The magic lies within machine learning algorithms. By feeding data into these algorithms, we guide them to recognize patterns and relationships hidden within the data. These algorithms can be trained to make predictions, classify data, or even generate new content.
Beyond Data & Algorithms
As AI advances, ethical and societal concerns become more paramount. We need to consider how AI will impact society, ensure fairness and accountability. Furthermore, the future of AI demands a focus on artificial general intelligence (AGI), an entity with the ability to surpass human intelligence in all aspects.

Start Your AI Adventure
This is just a glimpse into the vast world of AI. By understanding its fundamentals, data principles, and application across industries, you're well-equipped to embark on your own AI adventure. Remember, the more you explore and learn about this dynamic field, the more you'll discover its potential to reshape our world in profound ways.